In the following article we are going to integrate spring cloud contract testing into a new microservice (producer) and we will create another microservice that will act as a consumer.

- Producer service configuration
We will use bonus-service and configure it to create the contract stubs and and automatically generated producer test that verifies our API contract.
Service has no contract testing integration but in the following steps we will :
- Add contract testing dependency and maven contract plugin
- Create base test class for autogenerated tests
- Create contract for one of our endpoints
Adding the dependencies in the pom file
a. spring-cloud-starter-contract-verifier
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-contract-verifier</artifactId>
<version>2.2.4.RELEASE</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>b. Maven plugin
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<baseClassForTests>
com.bonus.service.contract.BaseTestClass
</baseClassForTests>
</configuration>
</plugin>NOTE: Select dependency according to your spring boot version
Create BaseTestClass for your controller
The location of the class needs to be according to what we set in the maven plugin area : com.bonus.service.contract.BaseTestClas
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.MOCK)
@DirtiesContext
@AutoConfigureMessageVerifier
public class BaseTestClass {
@Autowired
BonusController bonusController;
@Before
public void setBonusController(){
StandaloneMockMvcBuilder standaloneMockMvcBuilder = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(bonusController);
RestAssuredMockMvc.standaloneSetup(standaloneMockMvcBuilder);
}
}Create contract for one of our endpoints
When running the bonus-service application we can reach swagger-ui by using our localhost
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.htm

Using getAllBonuses endpoint will give us a list of bonuses available (use addBonus to create one before using getAllBonuses, use startTime and endTime according to contract bellow)
Contract location: src/test/resources/contracts/shouldGetBonus.groovy
import org.springframework.cloud.contract.spec.Contract
Contract.make {
description("Should return a bonus")
request {
method GET()
url("/bonus/getAllBonuses")
}
response {
body(
[
"id" : $(c(1), p(anyPositiveInt())),
"bonusName": $(c("You got an iPhone"), p(anyNonEmptyString())),
"bonusType": $(c("Reward Bonus"), p(anyNonEmptyString())),
"startTime": $(c("2020-10-10"), p(anyNonEmptyString())),
"endTime" : $(c("2023-10-10"), p(anyNonEmptyString())),
]
)
status(200)
}
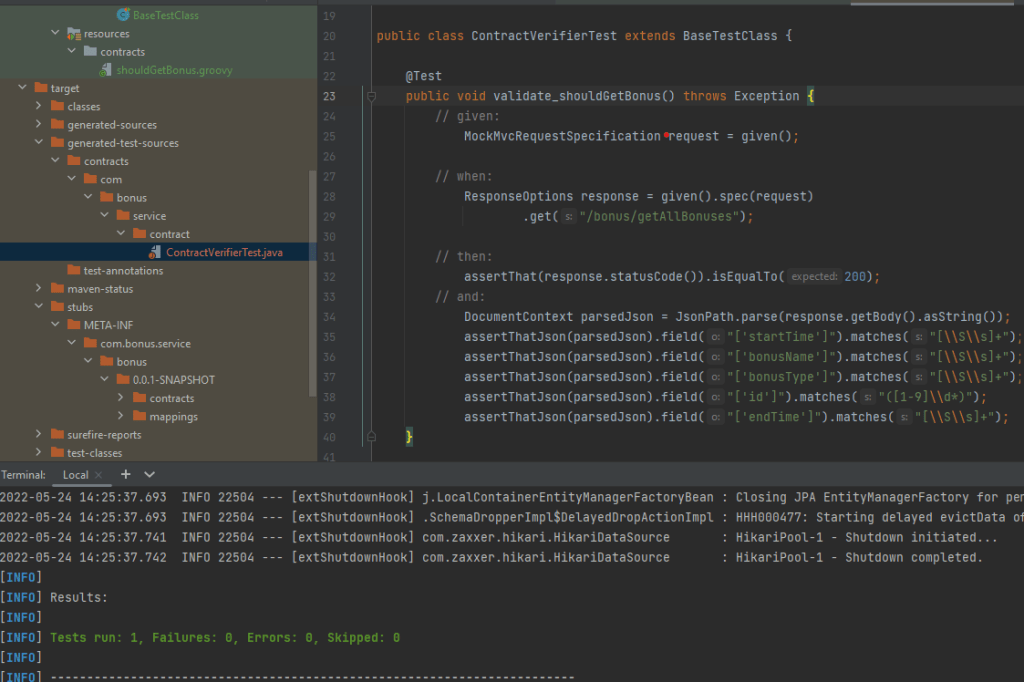
}Running mvn clean install on the bonus-service project will generate the stubs and automatically create a test class that checks the contract fields
2. Consumer service configuration
We will create our consumer service using https://start.spring.io/ and open the project into IDE
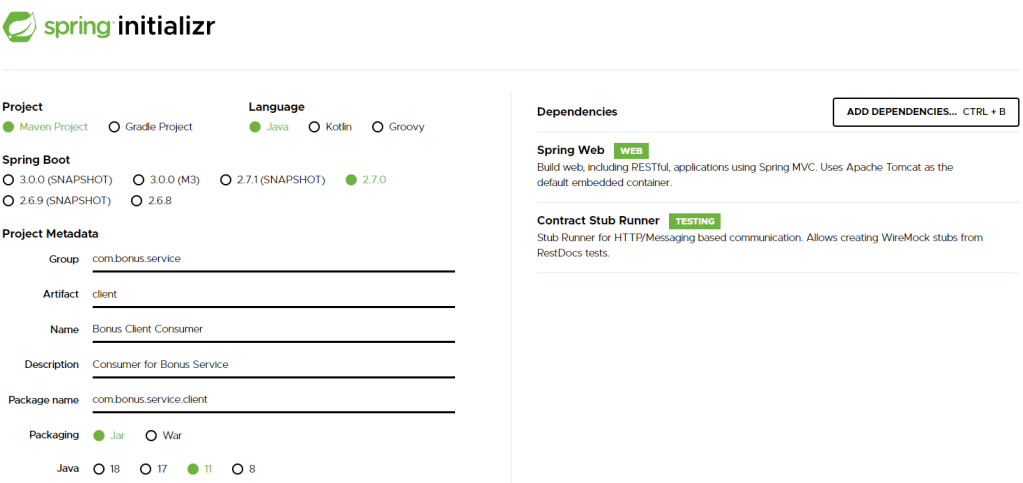
The dependency that allows us to create the consumer test on the contract is
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
dependency>Now let’s create the spring cloud contract consumer test
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.MOCK)
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(
stubsMode = StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.LOCAL,
ids = "com.bonus.service:bonus:+:stubs:8090")
class BonusClientConsumerApplicationTests {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
@Test
void getAllBonuses() throws Exception {
ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.getForEntity("http://localhost:8090/bonus/getAllBonuses", String.class);
Assertions.assertEquals(response.getStatusCode().is2xxSuccessful(), true);
Assertions.assertEquals(response.getBody().contains("Super iPhone"), true);
}
}Now let’s break them and explain stubrunner properties
- StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.LOCAL
Setting the StubMode to LOCAL means that the stubrunner will search for stubs located into our LOCAL M2 maven repository according to the ids property
- ids = “com.bonus.service:bonus:+:stubs:8090”
Inside of the M2 repository the stubrunner will search for path com/bonus/service/bonus and use the latest version (+), import the stubs into wiremock and start the server on port 8090
Now let’s run the test and see what happens
In the console we can see the following important logs
Use stubs from local repository
Will download stubs and contracts via Aether
Remote repos not passed but the switch to work offline was set. Stubs will be used from your local Maven repository.
Desired version is [+] - will try to resolve the latest version
Resolved version is [0.0.1-SNAPSHOT]Add into wiremock server /ping and /health and our contract stub
127.0.0.1 - POST /mappings
Host: []
Content-Length: [423]
Content-Type: [text/plain; charset=UTF-8]
Connection: [keep-alive]
User-Agent: [Apache-HttpClient/5.1.3 (Java/11.0.15)]
{
"id" : "65b1a352-f0ca-4b70-bdaf-79fc9ea54889",
"request" : {
"url" : "/bonus/getAllBonuses",
"method" : "GET"
},
"response" : {
"status" : 200,
"body" : "{\"bonusName\":\"Super iPhone\",\"startTime\":\"2020-10-10\",\"id\":1,\"endTime\":\"2023-10-10\",\"bonusType\":\"Super Bonus\"}",
"transformers" : [ "response-template" ]
},
"uuid" : "65b1a352-f0ca-4b70-bdaf-79fc9ea54889"
}Start the stub server using our contract
Started stub server for project [com.bonus.service:bonus:0.0.1-SNAPSHOT:stubs] on port 8090 with [1] mappingsExecute GET request from our test on the endpoint
WireMock : Request received:
127.0.0.1 - GET /bonus/getAllBonuses
Accept: [text/plain, application/json, application/*+json, */*]
User-Agent: [Java/11.0.15]
Host: [localhost:8090]
Connection: [keep-alive]
Matched response definition:
{
"status" : 200,
"body" : "{\"bonusName\":\"Super iPhone\",\"startTime\":\"2020-10-10\",\"id\":1,\"endTime\":\"2023-10-10\",\"bonusType\":\"Super Bonus\"}",
"transformers" : [ "response-template" ]
}
Response:
HTTP/1.1 200
Matched-Stub-Id: [65b1a352-f0ca-4b70-bdaf-79fc9ea54889]A few improvements can be done to the consumer and producer services like defining dynamic ports for stubrunner and wiremock server , create a application.properties where to configure test configuration and setup REMOTE stub download for consumer but the article is presenting how easy is to integrate contract testing into Java services with spring cloud contract dependencies.
Keep learning and have fun doing it 🙂






Leave a comment