U
Microservice with JPA and in memory H2 database
Short description
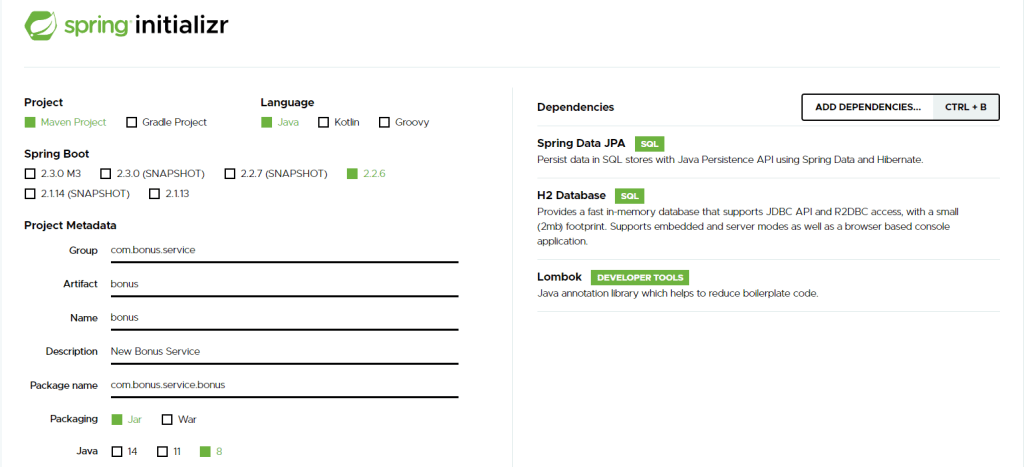
- The first thing that we need to do in order to fast start a spring boot microservice is to use the start.spring.io website
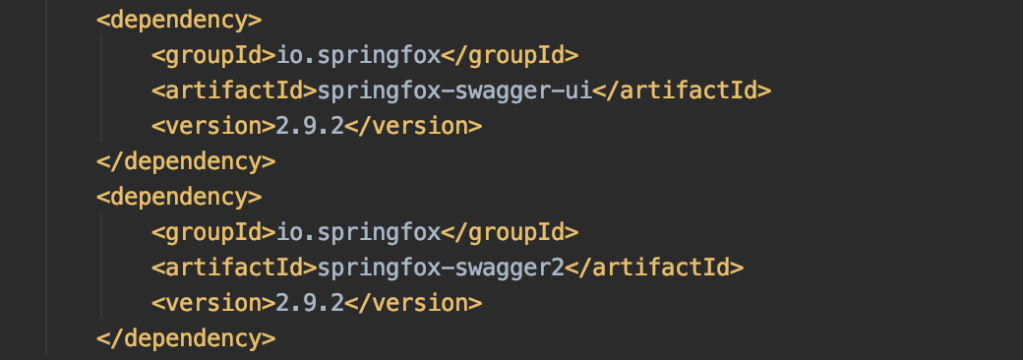
Add swagger dependencies in the main pom file since we will configure it later for testing:
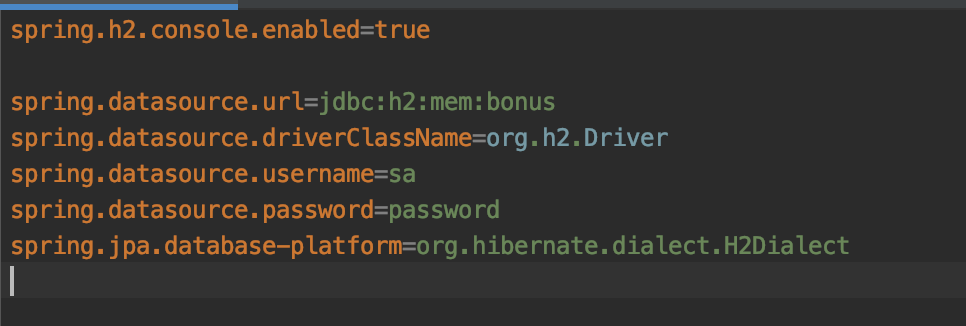
Configure service H2 database
The service will use the H2 in memory database and this can be setup with the following properties
Create a schema.sql file into the resources folder and define the table structure

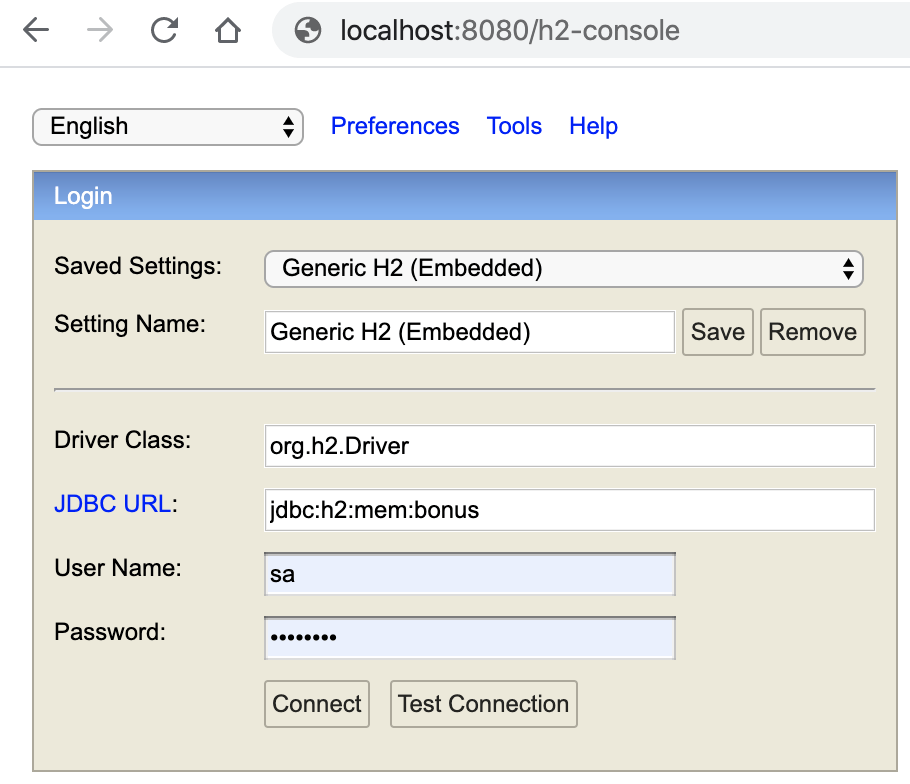
Now that the basic configuration for the database has been set we can start the microservice and access database by using the H2 console, login with the user and password that we set into the properties file
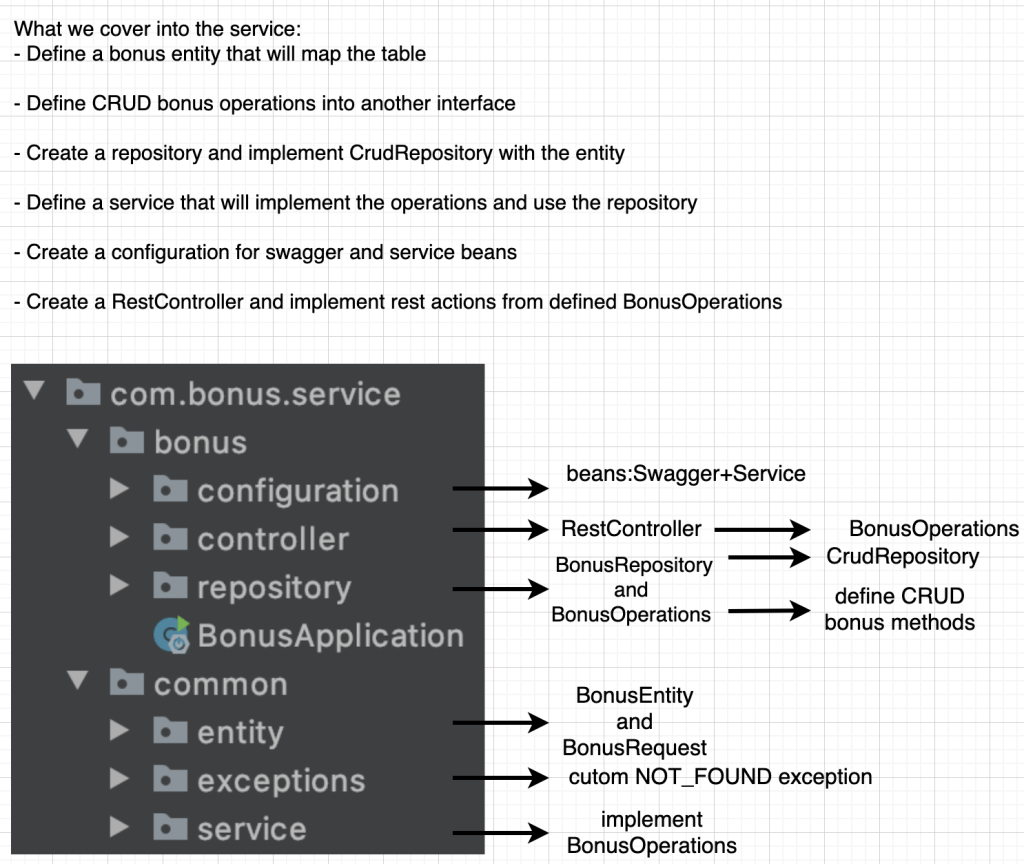
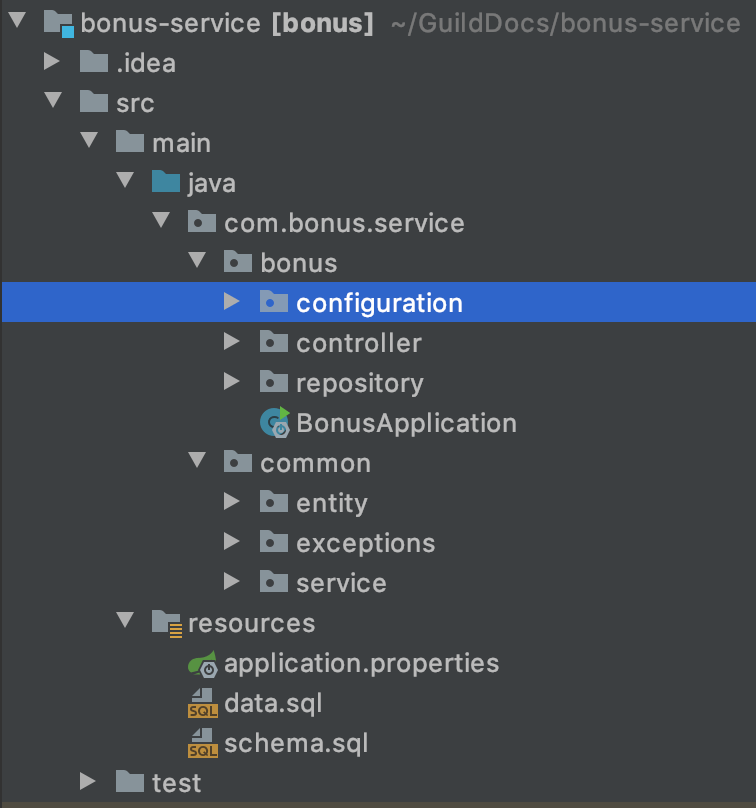
Define service packages and start coding
Create the packages according to the picture bellow and lets add some code in each one
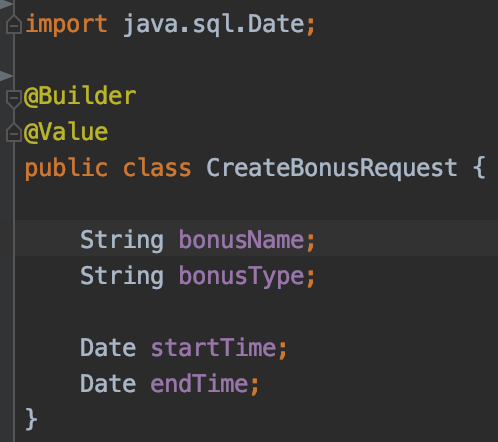
1.Define the class entity and the bonus request that we will use in order to create the bonus
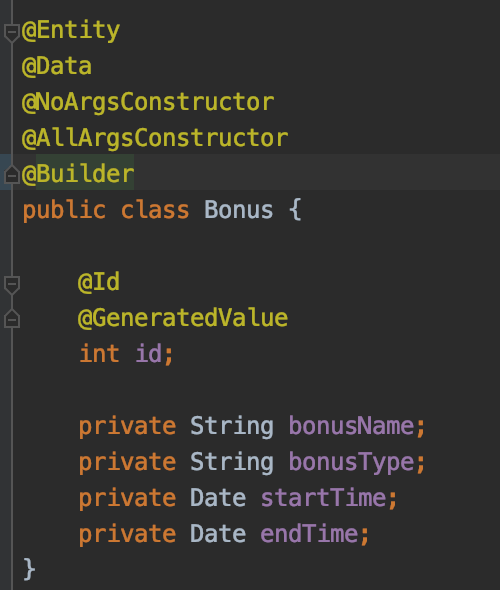
- @Entity – defines for which table the class will be mapped,
- @Id annotation is used to map the primary key of the table
- @GeneratedValue – the value of this field will be autogenerated.The default strategy used to generate the number is GenerationType.AUTO
All the other lombok annotations are used to remove boilerplate code ->https://projectlombok.org/features/all
NOTE:The name of the class should map the name of the table.In case of other class names user should define the table name using @Table(name = “bonus”) annotation
2. Define bonus repository and operations that we will use
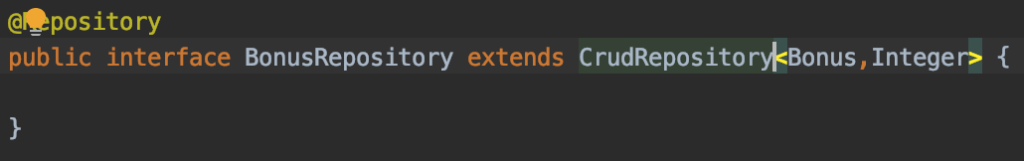
The CrudRepository interface already provides out of the box CRUD methods but we will have a better view of our operations is we define them into another interface and implement them using CrudRepository
CRUD operations
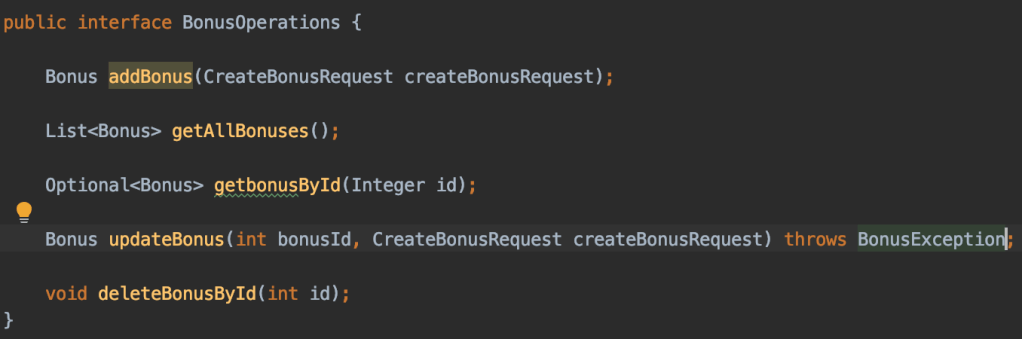
3. Implement CRUD operations into the service class
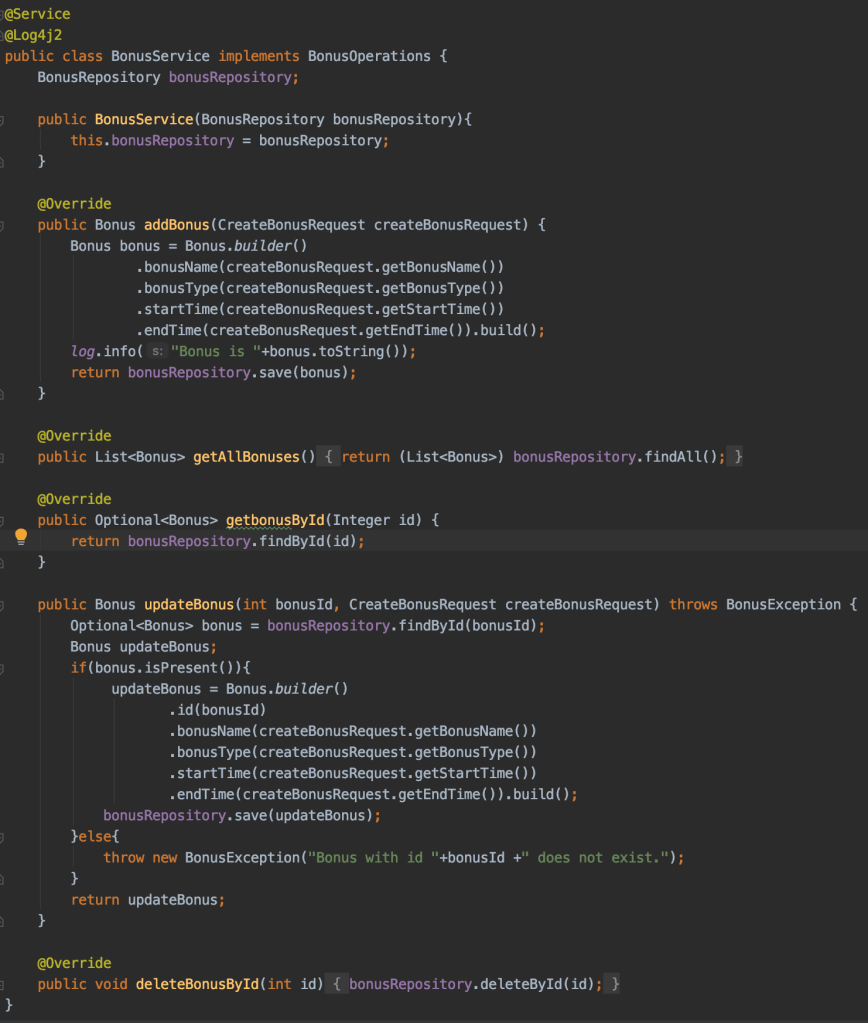
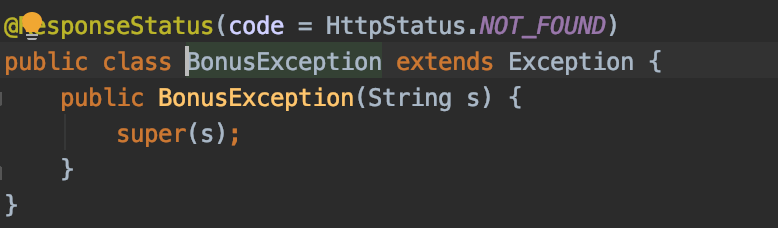
And let’s not forget about our bonus exception which replies with a 404 when we try to update an invalid bonus id
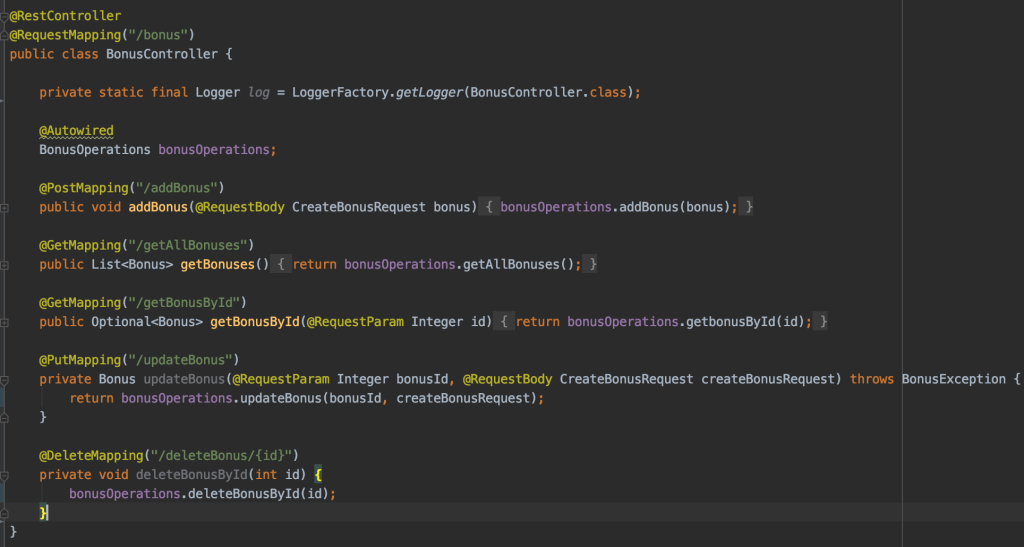
4. Create the controller and define the RestAPI actions
5.Create configuration class for swagger functionality